Mesothelioma Types
Mesothelioma, a devastating cancer, primarily targets the mesothelium, a delicate membrane enveloping the body’s internal organs.
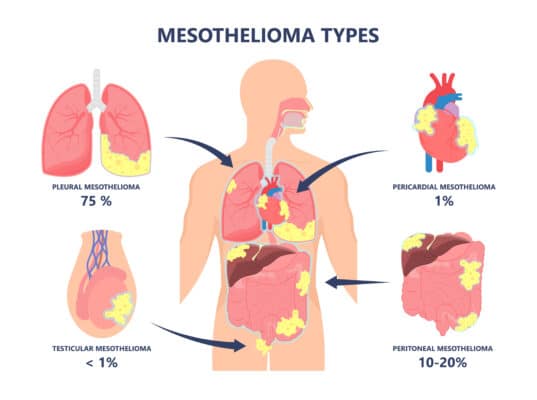
Mesothelioma manifests in diverse forms, depending on its location within the body. The most prevalent type is pleural mesothelioma, which affects the pleural mesothelium enveloping the lungs. Pleural mesothelioma constitutes approximately 75% of all mesothelioma cases.
Peritoneal mesothelioma, arising in the abdominal lining, accounts for 10-20% of diagnoses. On the rarer end of the spectrum, we encounter pericardial mesothelioma, impacting the heart, and testicular mesothelioma, affecting the testicles.
Cellular Structures
Physicians classify mesothelioma further by examining the shape and structure of cancer cells, revealing distinct characteristics. There are four primary cellular classifications:
- Epithelioid Mesothelioma: Representing about 60% of diagnosed cases, this type showcases uniform and well-structured cells resembling epithelial cells found in various bodily glands.
- Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma: Constituting merely 10% of diagnoses, sarcomatoid mesothelioma displays irregular, spindle-shaped cells with overlapping patterns under a microscope.
- Desmoplastic Mesothelioma: A variant of sarcomatoid mesothelioma, desmoplastic cells appear innocuous and can be misdiagnosed as benign fibrous tissue.
- Biphasic Mesothelioma: With roughly 30% of diagnoses, biphasic mesothelioma presents tumors comprised of both epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells.
Treatment Considerations
Treatment decisions for mesothelioma are primarily determined by the tumor’s location within the body, rather than the type of cancer cells present. Different cell types respond variably to treatments, influences the aggressiveness of treatment strategies. It is important to personalize care for each mesothelioma patient.
